QuBi/modules/biol302: Difference between revisions
imported>Ppagan No edit summary |
imported>Ppagan No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
[[File:4seq.png]] | [[File:4seq.png]] | ||
===Questions=== | ===[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Exit_Questions|Exit Questions]]=== | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 21 February 2013
BIOL 302 Lab: Bioinformatics Exercises
[Link to BIOL302 page, if one exists]
Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST
Objectives
- Learn to use Genbank database and BLAST tool to analyze nucleotide sequences
- Use BLAST to identify
Key Concepts
Blast
Alternative Splicing
Exercise
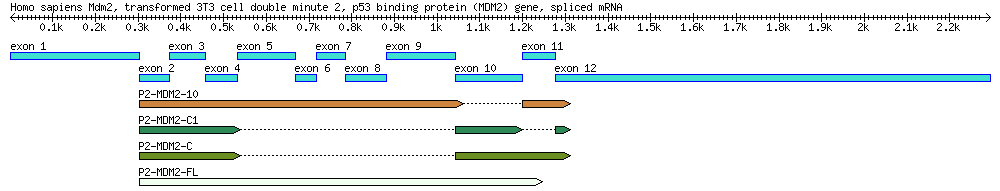
| Genbank Accession # | cDNA Clone | Description | Cell Line | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF527840 | Genomic DNA | 34,088 | ||
| EU076746 | P2-MDM2-C1 | cDNA missing exons 5-9 & 11 | MANCA | 427 |
| EU076747 | P2-MDM2-10 | cDNA missing exon 10 | ML-1 | 842 |
| EU076748 | P2-MDM2-C | cDNA missing exons 5-9 | A876 | 505 |
| EU076749 | P2-MDM2-FL | Full-length cDNA | SJSA-1 | 845 |
- Explore the annotation for AF527840.
The sequences on the genbank database have annotations associated with them. Some sequences are richly annotated to contain all of the details you would want, and other sequences may have almost no annotations at all. The sequence you are about to explore is well annotated with details such as exon locations and nucleotide variablility. Use the annotations to complete the following tasks and questions.
1) DRAW a diagram of this gene, including its introns/exons, 3'/5' UTRs, +1. (Note: this diagram is going to be very handy for the last set of questions.) - Label each feature with its coordinates. For example, if an exon starts at 500bp and ends at 1000bp, label it as such. - Label the diagram with basic information, such as the gene's name and th organism's species. - The drawing does not have to be exactly to scale, a reasonable effort should be made to do so. Put length markers on your drawing (for example, every 5000bp.) - The mRNA annotation states which segments are used to create mRNA, and the CDS annotation states which parts actully code amino acids (CDS = coding sequence).
2) How does the sequence vary at positions X, X, and X for this gene?
3) What kinds of repeat regions can be found in this gene?