Bioutils: Difference between revisions
imported>Weigang |
imported>Weigang |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Print a brief help message and exit.</p> | <p>Print a brief help message and exit.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -h <keyword> | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt><b>--man, -m</b></dt> | <dt><b>--man, -m</b></dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Prints the manual page and exit.</p> | <p>Prints the manual page and exit.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -m <keyword> | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt><b>--input, -i</b> 'format'</dt> | <dt><b>--input, -i</b> 'format'</dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Input file format. By default, this is 'fasta'. For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.</p> | <p>Input file format. By default, this is 'fasta'. For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -i 'genbank' input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="output--o-format"><b>--output, -o</b> 'format'</dt> | <dt id="output--o-format"><b>--output, -o</b> 'format'</dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Output file format. By default, this is 'fasta'.For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.</p> | <p>Output file format. By default, this is 'fasta'.For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -o 'EMBL' input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="noseq--n"><b>--noseq, -n</b></dt> | <dt id="noseq--n"><b>--noseq, -n</b></dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Print number of sequences specified by n.</p> | <p>Print number of sequences specified by n.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -n input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="sub--s-min-max"><b>--sub, -s</b> 'min,max'</dt> | <dt id="sub--s-min-max"><b>--sub, -s</b> 'min,max'</dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Select substring (of 1st sequence),</p> | <p>Select substring (of 1st sequence),</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -s '<beginning index>, <ending index>' input_file | |||
Example: bioseq -s'20,80' input_file (or --sub'20,80' or -s='20,80' or --sub='20,80') | Example: bioseq -s'20,80' input_file (or --sub'20,80' or -s='20,80' or --sub='20,80') | ||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="lengths--l"><b>--lengths, -l</b></dt> | <dt id="lengths--l"><b>--lengths, -l</b></dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Print all sequence lengths.</p> | <p>Print all sequence lengths.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -l | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="leadgaps--y"><b>--leadgaps, -y</b></dt> | <dt id="leadgaps--y"><b>--leadgaps, -y</b></dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
<p>Count and return the number of leading gaps in each sequence.</p> | <p>Count and return the number of leading gaps in each sequence.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -y | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="pick--p-tag:value"><b>--pick, -p</b> 'tag:value'</dt> | <dt id="pick--p-tag:value"><b>--pick, -p</b> 'tag:value'</dt> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
<p>Select a single sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, e.g, --pick 'id:foo' by id --pick 'order:2' by order --pick 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected)</p> | <p>Select a single sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, e.g, --pick 'id:foo' by id --pick 'order:2' by order --pick 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected)</p> | ||
<p>Specifically for a list of sequences, --pick 'id:foo,bar' list by id --pick 'order:2,3' list by order --pick 'order:2-10' list by range</p> | <p>Specifically for a list of sequences, --pick 'id:foo,bar' list by id --pick 'order:2,3' list by order --pick 'order:2-10' list by range</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -p 'id:<number>' input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
<dt id="del--d-tag:value"><b>--del, -d</b> 'tag:value'</dt> | <dt id="del--d-tag:value"><b>--del, -d</b> 'tag:value'</dt> | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
Delete a sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, eg, | |||
--del 'id:foo' by id | --del 'id:foo' by id | ||
--del 'order:2' by order | --del 'order:2' by order | ||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
--del 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected) | --del 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected) | ||
Usage: bioseq --del 'id:<number>' input_file | Usage: bioseq --del 'id:<number>' input_file | ||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
<p>Reverse complement</p> | <p>Reverse complement</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -r input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
<p>Generate overlapping subsequence with a specified window size (default 1)</p> | <p>Generate overlapping subsequence with a specified window size (default 1)</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -k '<index of subsequence>' input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
<p>Translate in 1, 3, or 6 frames. eg, -t1, -t3, or -t6.</p> | <p>Translate in 1, 3, or 6 frames. eg, -t1, -t3, or -t6.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -t3 input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
<p>Shred into individual sequences</p> | <p>Shred into individual sequences</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -c input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 170: | Line 170: | ||
<p>Linearize FASTA.</p> | <p>Linearize FASTA.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -L fasta_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
<p>Extract in-frame sequences.</p> | <p>Extract in-frame sequences.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -e input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
<p>Remove gaps</p> | <p>Remove gaps</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -g input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 194: | Line 194: | ||
<p>Output the frame that gives the longest ORF.</p> | <p>Output the frame that gives the longest ORF.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -C input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
<p>Remove stop codons (for e.g., PAML input)</p> | <p>Remove stop codons (for e.g., PAML input)</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -x input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
<p>Replace sequence IDs with serial IDs 'n' characters long, including a leading 'S' (e.g., -a'5' gives S0001). Produces a sed script file with a '.sed' suffix that may be used with sed's '-f' argument. If the filename is '-', the sed file is named STDOUT.sed instead. The sed filename is specified on STDERR.</p> | <p>Replace sequence IDs with serial IDs 'n' characters long, including a leading 'S' (e.g., -a'5' gives S0001). Produces a sed script file with a '.sed' suffix that may be used with sed's '-f' argument. If the filename is '-', the sed file is named STDOUT.sed instead. The sed filename is specified on STDERR.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -a <number> input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
<p>If there are enough sequences that the length of the prefix plus the length of the digit portion exceeds the length given to --anonymize, a warning will be given: aln-manipulations.pl -a 4 --prefix=SEQ # output SEQ1 atg... ... SEQ10 atc...</p> | <p>If there are enough sequences that the length of the prefix plus the length of the digit portion exceeds the length given to --anonymize, a warning will be given: aln-manipulations.pl -a 4 --prefix=SEQ # output SEQ1 atg... ... SEQ10 atc...</p> | ||
# more output | |||
WARNING: Anonymized ID length exceeded requested length: try a different length or prefix. | WARNING: Anonymized ID length exceeded requested length: try a different length or prefix. | ||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
<p>Base or AA composition.</p> | <p>Base or AA composition.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -w input_file | |||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 237: | Line 237: | ||
<p>Split the input sequence file into several smaller files with 'split_at' sequences per file. For instance, to split a file into several smaller files with 100000 sequences each, you would run:</p> | <p>Split the input sequence file into several smaller files with 'split_at' sequences per file. For instance, to split a file into several smaller files with 100000 sequences each, you would run:</p> | ||
bioseq -S 100000 seq.fasta | |||
<p>The output files will be named with the label "split_N" according to the input file (or with the STDIN prefix if the file is read via standard in), where N denotes the "part" or "split" number.</p> | <p>The output files will be named with the label "split_N" according to the input file (or with the STDIN prefix if the file is read via standard in), where N denotes the "part" or "split" number.</p> | ||
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
<dd> | <dd> | ||
Usage: bioseq -z [Accession] | |||
Retrieves the sequence from GenBank using the provided GenBank accession. Prints out text in a fasta file. | Retrieves the sequence from GenBank using the provided GenBank accession. Prints out text in a fasta file. | ||
| Line 265: | Line 265: | ||
AAAACACATGGGACTAACGATAAGGGTGCTAAAGAACTTAAAGAGTTATCTGAATCAGTA | AAAACACATGGGACTAACGATAAGGGTGCTAAAGAACTTAAAGAGTTATCTGAATCAGTA | ||
GAAAGCTTGGCAAAAGCAGCTCAAGCAGCATTAGCTAATTCAGTTAAAGAGCTTACAAGT | GAAAGCTTGGCAAAAGCAGCTCAAGCAGCATTAGCTAATTCAGTTAAAGAGCTTACAAGT | ||
CCTGTTGTGGCAGAAAGTCCAAAAAAACCTTAA | CCTGTTGTGGCAGAAAGTCCAAAAAAACCTTAA | ||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 273: | Line 273: | ||
<p>Extract two sequences from input file and generate a dotplot.</p> | <p>Extract two sequences from input file and generate a dotplot.</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -D 'id1,id2,window_size,slider' fasta_file | |||
<p>Id1 and Id2 are extracted with their corresponding sequences. Be sure to use the entire sequence identifer, as this is a whole string match. Window_size corresponds to the number of character you would like to compare (Default window is 10). Slider is the number of windows to compare (Default slider is 10). The sequence corresponding to ID1 will appear on the X axis (row) and ID2 on the Y axis (column). This method will work on both DNA and Amino Acids.</p> | <p>Id1 and Id2 are extracted with their corresponding sequences. Be sure to use the entire sequence identifer, as this is a whole string match. Window_size corresponds to the number of character you would like to compare (Default window is 10). Slider is the number of windows to compare (Default slider is 10). The sequence corresponding to ID1 will appear on the X axis (row) and ID2 on the Y axis (column). This method will work on both DNA and Amino Acids.</p> | ||
Example: | |||
Sample Input: | Sample Input: | ||
>id1 | >id1 | ||
| Line 300: | Line 300: | ||
A | A | ||
T | T | ||
G | G | ||
<p><b>--rename, -R</b> 'rename_id'</p> | <p><b>--rename, -R</b> 'rename_id'</p> | ||
Usage: bioseq -R [file_with_new_names] file_to_be_changed.fasta | |||
Ex: bioseq -D list.txt test-bioseq.nuc | Ex: bioseq -D list.txt test-bioseq.nuc | ||
| Line 332: | Line 332: | ||
>B31 | >B31 | ||
AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA | AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA | ||
TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA | TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA | ||
</dd> | </dd> | ||
| Line 347: | Line 347: | ||
* SEE ALSO | * SEE ALSO | ||
perl(1) | |||
* AUTHORS | * AUTHORS | ||
Weigang Qiu at genectr.hunter.cuny.edu | |||
Yözen Hernández yzhernand at gmail dot com | |||
Levy Vargas levy dot vargas at gmail dot com | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 19:31, 29 September 2014
BioPerl-based Sequence Utilities
What is bioutils?
bioutils is a suite of Perl scripts that provide convenient command-line access to popular BioPerl methods. Designed as UNIX utilities, these tools aim to circumvent a constant need (and urge) for composing one-off BioPerl scripts for routine manipulations of sequences, alignments and trees.
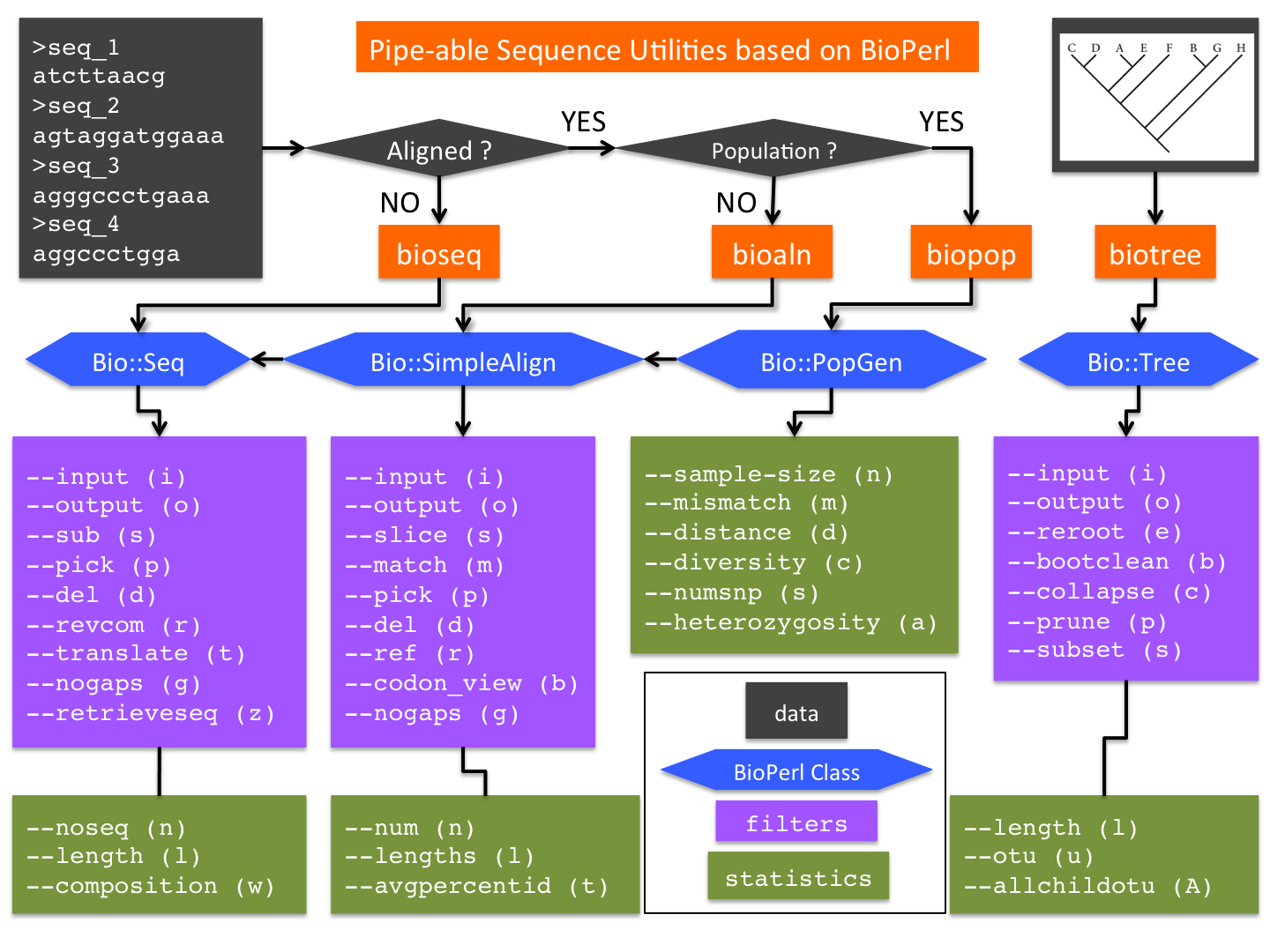
The initial release of bioutils consists of four utilities (Figure 1):
- bioseq: a wrapper of BioPerl class Bio::Seq (with additional methods)
- bioaln: a wrapper of Bio::SimpleAlign (which inherits Bio::Seq; with additional methods)
- biopop: a wrapper of Bio::PopGen (which can be converted from Bio::SimpleAlign; with additional methods)
- biotree: a wrapper of Bio::tree (with additional methods)
These utilities have been in development since 2002 in the lab of Dr Weigang Qiu at Hunter College of the City University of New York. They are the main code base of the Qiu Lab, which specializes in microbial evolutionary genomics. They proved to be convenient, efficient, and popular among students and researchers passing through the lab. By releasing bioutils as an Open Source tool (perhaps as a part of bioperl distribution), we hope to (1) share our experience and (2) invite other developers to join the effort of making BioPerl more accessible.
Live Demos
Basic Usage
- bioseq
bioseq -l foo.fasta # print seq names and lengths from FASTA (default format) file
bioseq -r foo.fasta # reverse complement
bioseq -t1 foo.fasta # translate in the +1 frame
bioseq -t3 foo.fasta # translate in +1, +2, and +3 frames
bioseq -t6 foo.fasta # translate in all 6 frames
bioseq -p'id:seq_1' foo.fasta # pick a sequence by ID
bioseq -p'order:3' # pick the 3rd sequence
bioseq -p're:Human' foo.fasta # pick all sequences labeled as "Human" (by regular expression)
bioseq -g foo.fasta # remove all gaps
bioseq -z'CP003201' -o'genbank' # retrieve a GenBank file with accession
bioseq -z'CP003201' -o'fasta' # same file in FASTA- bioaln
bioaln -i'fasta' -o'phylip' foo.fasta # convert a FASTA alignment to PHYLIP
bioaln -l foo.aln # print alignment length of a CLUSTALW (default format) file
bioaln -s'100, 200' foo.aln # obtain an alignment slice
bioaln -m foo.aln # show only variable sites
bioaln -r'seq_2' foo.aln # use "seq_2" as reference (first) sequence
bioaln -g foo.aln # remove gapped sites
bioaln -p'seq_1,seq_3,seq_6' foo.aln # pick a subset of sequences
bioaln -d'seq_1,seq_3,seq_6' foo.aln # delele a subset of sequences- biotree
- biopop
Power usage (with pipes)
# Pipe with the same utility
bioseq -p'order:5' foo.fasta | bioseq -s'100,200' | bioseq -r | bioseq -t1 # pick, subseq, revcom, and translate
# Pipe among utilities
bioaln -o'fasta' foo.aln | bioseq -g # remove gaps within individual sequencesCreative usage (with BASH utils)
echo -ne ">lookup\nATG\n" | bioseq -t1 # Lookup a codon product
len=$(bioaln -l foo.aln); len_degap=$(bioaln -g foo.aln | bioaln -l); echo "$len-$len_degap" | bc -l # count alignment gapsFull documentation
POD document for bioseq
- NAME
bioseq - Fasta sequence editing module based on BioPerl.
- SYNOPSIS
bioseq [options] [sequence file]
- DESCRIPTION
bioseq will read a sequence file and act upon it by doing the following - reformat input (default is fasta) to Genbank or EMBL formats, delete specified sequences, generate overlapping subsequence with a specified window size, generate the reverese complementary sequence, for nucleic acid sequences only, take input list of sequences apart into individual sequence files, extract a specified subset of the sequence, linearize the sequence, remove gaps, find the longest open reading frame (ORF), remove stop codons, give percentage composition of specified amino acids or nuclic acid bases, split the sequences as specified by the user, translate a specific frame of input sequence, or extract a specific gene ID from multiple file sequences. By default, bioseq will assume that both the input and the output are in FASTA format.
- OPTIONS
- --help, -h
-
Print a brief help message and exit.
Usage: bioseq -h <keyword>
- --man, -m
-
Prints the manual page and exit.
Usage: bioseq -m <keyword>
- --input, -i 'format'
-
Input file format. By default, this is 'fasta'. For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.
Usage: bioseq -i 'genbank' input_file
- --output, -o 'format'
-
Output file format. By default, this is 'fasta'.For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.
Usage: bioseq -o 'EMBL' input_file
- --noseq, -n
-
Print number of sequences specified by n.
Usage: bioseq -n input_file
- --sub, -s 'min,max'
-
Select substring (of 1st sequence),
Usage: bioseq -s '<beginning index>, <ending index>' input_file Example: bioseq -s'20,80' input_file (or --sub'20,80' or -s='20,80' or --sub='20,80') - --lengths, -l
-
Print all sequence lengths.
Usage: bioseq -l
- --leadgaps, -y
-
Count and return the number of leading gaps in each sequence.
Usage: bioseq -y
- --pick, -p 'tag:value'
-
Select a single sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, e.g, --pick 'id:foo' by id --pick 'order:2' by order --pick 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected)
Specifically for a list of sequences, --pick 'id:foo,bar' list by id --pick 'order:2,3' list by order --pick 'order:2-10' list by range
Usage: bioseq -p 'id:<number>' input_file
- --del, -d 'tag:value'
- Delete a sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, eg, --del 'id:foo' by id --del 'order:2' by order --del 'length:n' by min length, where 'n' is length --del 'ambig:x' by min % ambiguous base/aa, where 'x' is the % --del 'id:foo,bar' list by id --del 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected) Usage: bioseq --del 'id:<number>' input_file
- --revcom, -r
-
Reverse complement
Usage: bioseq -r input_file
- --slidingwindow, -k 'window_size'
-
Generate overlapping subsequence with a specified window size (default 1)
Usage: bioseq -k '<index of subsequence>' input_file
- --translate, -t [1|3|6]
-
Translate in 1, 3, or 6 frames. eg, -t1, -t3, or -t6.
Usage: bioseq -t3 input_file
- --shred, -c
-
Shred into individual sequences
Usage: bioseq -c input_file
- --linearize, -L
-
Linearize FASTA.
Usage: bioseq -L fasta_file
- --extract, -e
-
Extract in-frame sequences.
Usage: bioseq -e input_file
- --nogaps, -g
-
Remove gaps
Usage: bioseq -g input_file
- --longest-orf, -C
-
Output the frame that gives the longest ORF.
Usage: bioseq -C input_file
- --removestop, -x
-
Remove stop codons (for e.g., PAML input)
Usage: bioseq -x input_file
- --anonymize, -a 'n'
-
Replace sequence IDs with serial IDs 'n' characters long, including a leading 'S' (e.g., -a'5' gives S0001). Produces a sed script file with a '.sed' suffix that may be used with sed's '-f' argument. If the filename is '-', the sed file is named STDOUT.sed instead. The sed filename is specified on STDERR.
Usage: bioseq -a <number> input_file
- --prefix 'PREFIX'
-
Used in conjunction with --anonymize. This lets you specify a custom prefix for the anonymized sequence IDs given when using the --anonymize option. If this is given, then the whole prefix will count toward the total ID length. For example: suppose the prefix chosen is SEQ, and that for --anonymize you supplied 5. Then the maximum id length is 5, so there is room for only two more digits. e.g., SEQ01 atg... SEQ02 atg... SEQ03 atc...
If there are enough sequences that the length of the prefix plus the length of the digit portion exceeds the length given to --anonymize, a warning will be given: aln-manipulations.pl -a 4 --prefix=SEQ # output SEQ1 atg... ... SEQ10 atc...
# more output WARNING: Anonymized ID length exceeded requested length: try a different length or prefix.
- --composition, -w
-
Base or AA composition.
Usage: bioseq -w input_file
- --split, -S 'split_at'
-
Split the input sequence file into several smaller files with 'split_at' sequences per file. For instance, to split a file into several smaller files with 100000 sequences each, you would run:
bioseq -S 100000 seq.fasta
The output files will be named with the label "split_N" according to the input file (or with the STDIN prefix if the file is read via standard in), where N denotes the "part" or "split" number.
- --retrieveseq, -z 'sequence retriever using GenBank accession'
- Usage: bioseq -z [Accession] Retrieves the sequence from GenBank using the provided GenBank accession. Prints out text in a fasta file. EXAMPLE: bioseq -z X83553 OUTPUT: >X83553 B.garinii (PHei strain) opsC gene. ATGAAAAAGAATACATTAAGTGCGATATTAATGACTTTATTTTTATTTATATCTTGTAAT AATTCAGGTGGGGATACTGCATCTACTAATCCTGATGAGTCTGCGAAAGGACCTAATCTT ATAGAAATAAGCAAAAAAATTACAGATTCTAATGCATTTGTACTGGCTGTGAAAGAAGTT GAGGCTTTGATCTCATCTATAGATGAACTTGCTAATAAAGCTATTGGTAAAAAAATAAAT CAAAATGGTTTAGATGCTGATGCTAATCACAACGGATCATTGTTAGCAGGAGCCCATGCA ATATCAACTCTAATAAAACAAAAAACAGATGGATTGAAAGATCTAGAAGGGTTAAGTAAA GAAATTGCAAAGGTGAAGGAATGTTCCGATAAATTTACTAAAAAGCTAACAGATAGTCAT GCACAGCTTGGAGCAGTTGGTGGTGCTATTAATGATGATCGTGCAAAAGAAGCTATTTTA AAAACACATGGGACTAACGATAAGGGTGCTAAAGAACTTAAAGAGTTATCTGAATCAGTA GAAAGCTTGGCAAAAGCAGCTCAAGCAGCATTAGCTAATTCAGTTAAAGAGCTTACAAGT CCTGTTGTGGCAGAAAGTCCAAAAAAACCTTAA
- --dotplot, -D 'draw_dotplot'
-
Extract two sequences from input file and generate a dotplot.
Usage: bioseq -D 'id1,id2,window_size,slider' fasta_file
Id1 and Id2 are extracted with their corresponding sequences. Be sure to use the entire sequence identifer, as this is a whole string match. Window_size corresponds to the number of character you would like to compare (Default window is 10). Slider is the number of windows to compare (Default slider is 10). The sequence corresponding to ID1 will appear on the X axis (row) and ID2 on the Y axis (column). This method will work on both DNA and Amino Acids.
Example: Sample Input: >id1 ATACGA >id2 ATACGA
Command: bioseq -D 'id1,id2,3' Output:
A T A C G A A * T * A * C G A A C A A T G
--rename, -R 'rename_id'
Usage: bioseq -R [file_with_new_names] file_to_be_changed.fasta
Ex: bioseq -D list.txt test-bioseq.nuc
Input:
list.txt:
VS116:7:310:IGS:11 VS116 B31:1:100:IGS:11 B31
*Left column is the pattern to be replaced by the right column
file_to_be_changed.fasta:
>VS116:7:310:IGS:11 AATTTCAAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTGAAATTTTTCTAT TGGATAAATTCTATACAAGAAGGTAAATA >B31:1:100:IGS:11 AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA
Output: >VS116 AATTTCAAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTGAAATTTTTCTAT TGGATAAATTCTATACAAGAAGGTAAATA >B31 AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA
- EXAMPLES
Section under construction...
- REQUIRES
Perl 5.010, BioPerl
- SEE ALSO
perl(1)
- AUTHORS
Weigang Qiu at genectr.hunter.cuny.edu Yözen Hernández yzhernand at gmail dot com Levy Vargas levy dot vargas at gmail dot com
POD document for bioaln
POD document for biopop
POD document for biopop
Release 1.0 Notes
- Installation
- Dependency
Main contributors
- Yozen Hernandez
- Levy Vargas
- Pedro Pagan
- Che Martin
- James Haven
- Girish Ramrattan
- Raymond Liang
- Saymon Akther
- Daniel Packer
- Weigang Qiu