QuBi/modules/biol302
- BIOL 302 Lab (Bioinformatics Exercises)
Research in molecular genetics requires effective use of bioinformatic tools to analyze and understand the genetic materials being worked with. The following exercises will expose you to real-world scenarios and introduce you to the methods and tools you can use to solve these problems.
Part 1: Cloning of murine mdm2 gene sequence to study cis acting DNA elements
Key Concepts
- Homology searching using BLAST
- Mammalian gene enhancers
So far, you have excised this XbaI fragment:
TCTAGATGCATTTACGAAGGAGACAGAAAACGTCTTTCGGCAATAGCTCTCAAATGCAAAACGACGTCGG CGAGCTGTCCCTTACCTGGAGGCCCGCAGGAGAAGCGCGGTGATCCGAGAGGGTCCCCCAGGGGTGTCCG GTCGGTCTCCCGCTCGCCCAGCAGACGGCTGCGGAAACGGGGCAGCGTTTAAATAACCCCAGCTGGAGAC ATGTCAGGACTTAGCTCCTCCGACAGCCGACGCCGGACGTGTCCCAACTTGACCAGCCCCACAGGAAGAG CTGAGTCAACTCGGCCCAGCCCAGTCCCACCCGTCCCGGAAGCCGCATCCCGGCGAGTCCGGGACCAGGC ACCTGTCACCTCCTGGACCCCAGCAACGAGCCCAGCGCGACCCCGGAGCGGGCCCGAATTCTCTAGA
Identify gene using genome BLAST
- Go to the NCBI-BLAST website at NCBI/BLAST Home Page
- What is BLAST? Find the expanded answer by clicking on "more"
- Since BLAST finds matches (homologous sequences) between biological sciences, it needs a "query" sequence as input as well as a "database" to search against. To find the matches to the above sequence, what would be your "query" sequence and what would be your "database"?
- Start BLASTing against the mouse genome by clicking "Mouse" under "BLAST Assembled RefSeq Genomes"
- Copy and paste the above sequence into the "Enter Query Sequence" box
- Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click "BLAST"
- Wait for 10-30 seconds for the results to return (Be Patient). Once the result page is loaded, locate and copy the following information:
- Species and strain
- Chromosome
- Length of your query sequence
- Sequence identity, number of matched bases, and number of gaps between the matched sequences
- Full name of the gene that matches your query
- Click the link for "5' side" gene will bring you a standard GenBank file of this gene. Locate and copy the following structural information about this gene:
- Gene accession (ID number)
- Total length of the gene
- Number of introns
- Which is the actual coding strand (mRNA analog): the above sequence itself or its reverse complement?
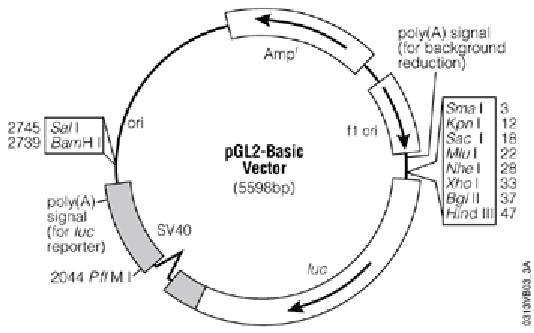
Explore pGL2 vector
This sequence has been cloned into the NheI site in the pGL2basic vector vector:
- Identify the location of insertion of this fragment
- From the PDF file, find the location of the EcoRI site
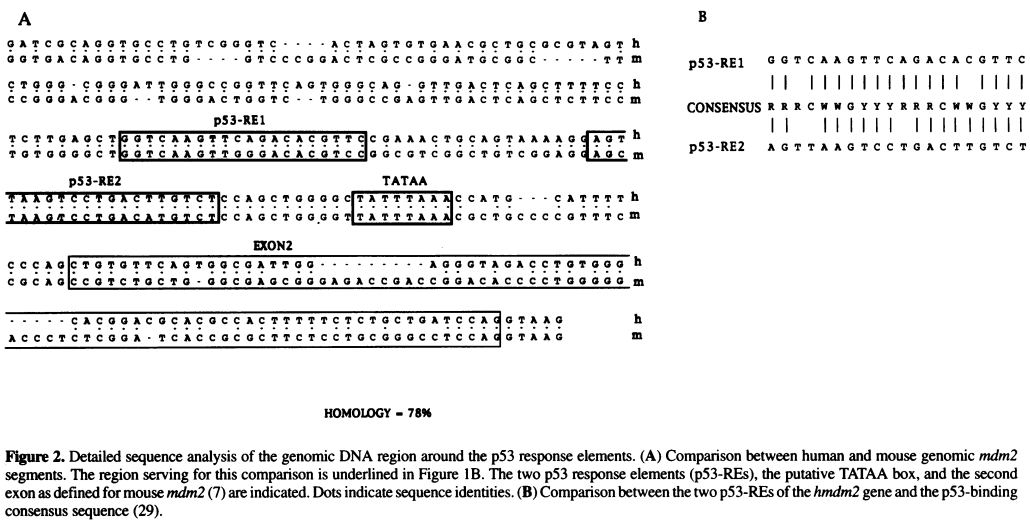
Identify functional elements in the above sequence
PROPERLY CITE THIS Taken from A functional p53-responsive intronic promoter is contained within the human mdm2 gene. Pubmed PDF
- Identify TATA box in the above sequence by looking for AT-rich regions
- Once the TATA box is located, use this sequence as the anchor point to locate other elements, including the 2 p53 Response Element (p53 RE) sites and the Exon 2
- Locate the EcoRI restriction site using the NEBcutter website
- What are the expected lengths of EcoRI-digested fragments if your clone is oriented correctly (i.e., upstream of the Luciferase gene)
- What if your cloned fragment is in the opposite direction (i.e., the TATA box situates downstream of the luciferase gene)
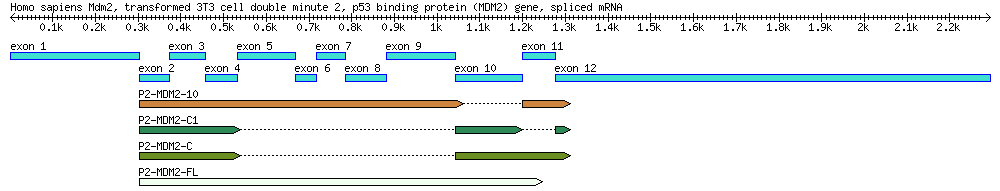
Part 1: Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST
A diagram of the MDM2 gene used in this exercise, along with its splice variants. By the end of this module you will create a similar diagram.
Objectives
- Learn to use Genbank database and BLAST tool to analyze nucleotide sequences
- Use BLAST to identify
Key Concepts
- Blast
- Genbank
- Annotation
- Accession Number
- Alternative Splicing
Exercise
| Genbank Accession # | cDNA Clone | Description | Cell Line | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF527840 | Genomic DNA | 34,088 | ||
| EU076746 | P2-MDM2-C1 | cDNA missing exons 5-9 & 11 | MANCA | 427 |
| EU076747 | P2-MDM2-10 | cDNA missing exon 10 | ML-1 | 842 |
| EU076748 | P2-MDM2-C | cDNA missing exons 5-9 | A876 | 505 |
| EU076749 | P2-MDM2-FL | Full-length cDNA | SJSA-1 | 845 |
- Explore the gene annotation for AF527840.
Sequences on genbank have both basic reference information (such as what the sequence is, what organism it came from, and bibliographical information) and sequence annotations. Some sequences are more richly annotated than others - it is up to researchers to annotate the sequences they generate, which requires extra work. For this exercise you will be working will a well-annotated sequence: accession number AF527840. Explore its annotation and use it to complete the following set of tasks.
- DRAW a diagram of this gene using the information and coordinates listed in the annotation. (Note: this is the bulk of the assignment and this diagram is needed for the last set of questions. Don't get lazy on this.)
- Label the top of the diagram with basic information, such as the gene's name, organism, etc.. Someone should be able to pick up your diagram and know exactly what they're looking at.
- Including introns, exons, 3'/5' UTRs, +1, and exact coordinates. (The mRNA annotation states which segments are used to create mRNA, and the CDS annotation states which parts code amino acids (CDS = coding sequence)).
- Draw the diagram mostly to scale. It does NOT have to be perfect, but make a reasonable effort. Put a scale bar and length markers on your drawing.
- How does the sequence vary at positions X, X, and X for this gene? Do these change the AA for the resulting peptide?
- What kinds of repeat regions can be found in this gene?
- Explore the graphical presentation of the gene to answer the following question.
Genbank provides graphical representations of the sequences on its database: click the "Graphics" link below the sequence title, OR click "Display Settings" above the title, and choose "Graphics". Take a few minutes to explore this graphical browser and answer the following question:
- A question that can only be answered from looking at this graph.
- Another question that can only be answered from looking at this graph.
- Use BLAST to determine which exons are used in the mRNA transcripts.
This is the most "bioinformatic" part of the assignment. Blast ALL FOUR of the mRNA sequences (EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749) against the main sequence (AF527840) and use the results to answer the following questions. If you labeled your diagram well (with coordinates!), this task should go by quickly.
- Which exons are used to create EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749?
- Do the BLAST search results corresponding to exons exactly match the start/end positions of the exons as labeled in your diagram? If not, what is the most likely reason for this?
- Do any of the BLAST results match regions outside of exons? If so, what regions?