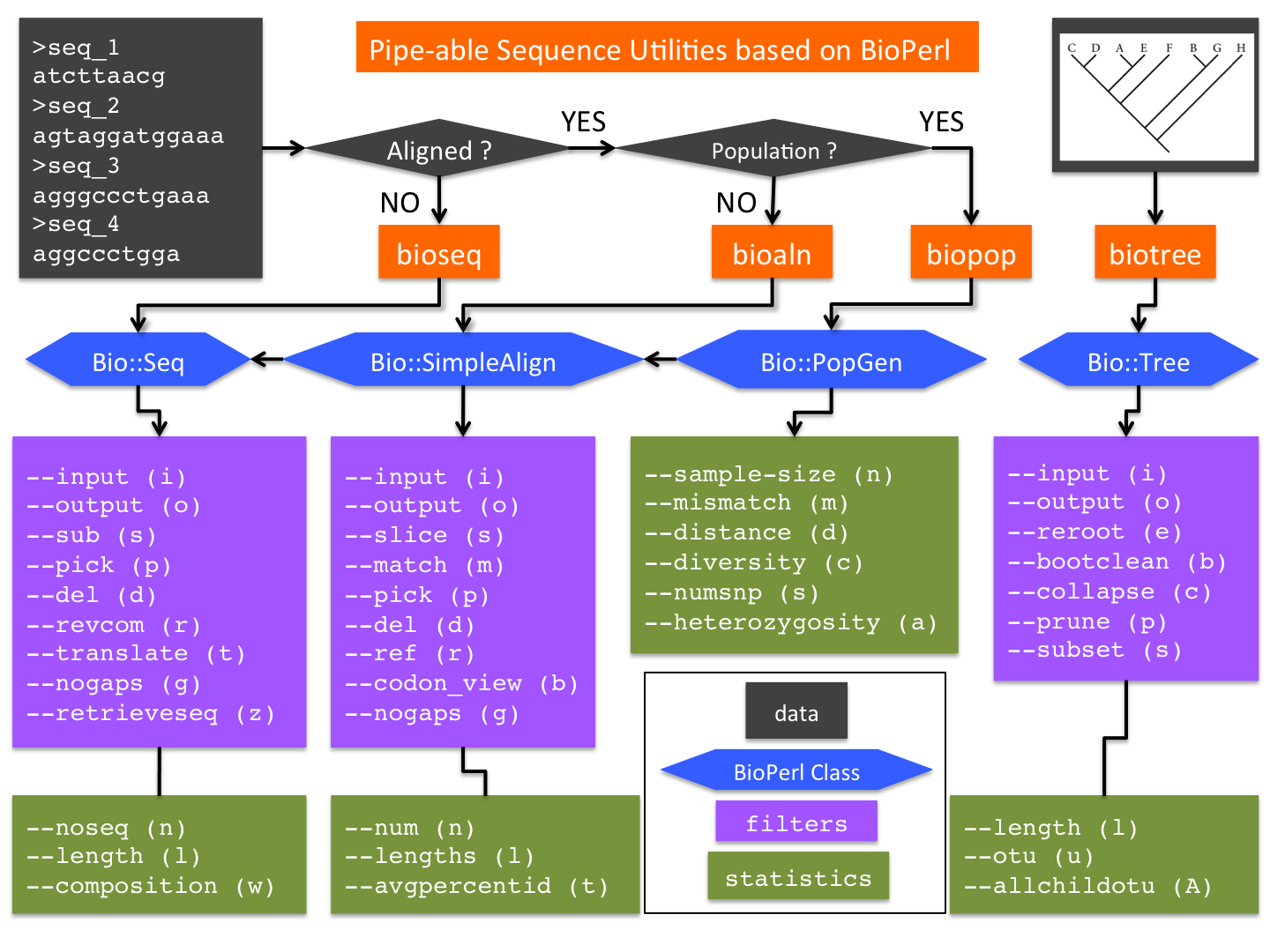
bioseq - Fasta sequence editing module based on BioPerl.
- --help, -h
-
Print a brief help message and exit.
<code> Usage: bioseq -h <keyword></code>
- --man, -m
-
Prints the manual page and exit.
<code> Usage: bioseq -m <keyword> </code>
- --input, -i 'format'
-
Input file format. By default, this is 'fasta'. For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.
<code> Usage: bioseq -i 'genbank' input_file</code>
- --output, -o 'format'
-
Output file format. By default, this is 'fasta'.For Genbank format, use 'genbank'. For EMBL format, use 'embl'.
<code> Usage: bioseq -o 'EMBL' input_file</code>
- --noseq, -n
-
Print number of sequences specified by n.
<code> Usage: bioseq -n input_file</code>
- --sub, -s 'min,max'
-
Select substring (of 1st sequence),
<code> Usage: bioseq -s '<beginning index>, <ending index>' input_file
Example: bioseq -s'20,80' input_file (or --sub'20,80' or -s='20,80' or --sub='20,80')</code>
- --lengths, -l
-
Print all sequence lengths.
<code> Usage: bioseq -l</code>
- --leadgaps, -y
-
Count and return the number of leading gaps in each sequence.
<code> Usage: bioseq -y</code>
- --pick, -p 'tag:value'
-
Select a single sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, e.g, --pick 'id:foo' by id --pick 'order:2' by order --pick 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected)
Specifically for a list of sequences, --pick 'id:foo,bar' list by id --pick 'order:2,3' list by order --pick 'order:2-10' list by range
<code> Usage: bioseq -p 'id:<number>' input_file</code>
- --del, -d 'tag:value'
-
<code> Delete a sequence or a comma-separated list of sequences, eg,
--del 'id:foo' by id
--del 'order:2' by order
--del 'length:n' by min length, where 'n' is length
--del 'ambig:x' by min % ambiguous base/aa, where 'x' is the %
--del 'id:foo,bar' list by id
--del 're:REGEX' using a regular expression (only one regex is expected)
Usage: bioseq --del 'id:<number>' input_file</code>
- --revcom, -r
-
Reverse complement
<code> Usage: bioseq -r input_file</code>
- --slidingwindow, -k 'window_size'
-
Generate overlapping subsequence with a specified window size (default 1)
<code> Usage: bioseq -k '<index of subsequence>' input_file</code>
- --translate, -t [1|3|6]
-
Translate in 1, 3, or 6 frames. eg, -t1, -t3, or -t6.
<code> Usage: bioseq -t3 input_file</code>
- --shred, -c
-
Shred into individual sequences
<code> Usage: bioseq -c input_file</code>
- --linearize, -L
-
Linearize FASTA.
<code> Usage: bioseq -L fasta_file</code>
-
Extract in-frame sequences.
<code> Usage: bioseq -e input_file</code>
- --nogaps, -g
-
Remove gaps
<code> Usage: bioseq -g input_file</code>
- --longest-orf, -C
-
Output the frame that gives the longest ORF.
<code> Usage: bioseq -C input_file</code>
- --removestop, -x
-
Remove stop codons (for e.g., PAML input)
<code> Usage: bioseq -x input_file</code>
- --anonymize, -a 'n'
-
Replace sequence IDs with serial IDs 'n' characters long, including a leading 'S' (e.g., -a'5' gives S0001). Produces a sed script file with a '.sed' suffix that may be used with sed's '-f' argument. If the filename is '-', the sed file is named STDOUT.sed instead. The sed filename is specified on STDERR.
<code> Usage: bioseq -a <number> input_file</code>
- --prefix 'PREFIX'
-
Used in conjunction with --anonymize. This lets you specify a custom prefix for the anonymized sequence IDs given when using the --anonymize option. If this is given, then the whole prefix will count toward the total ID length. For example: suppose the prefix chosen is SEQ, and that for --anonymize you supplied 5. Then the maximum id length is 5, so there is room for only two more digits. e.g., SEQ01 atg... SEQ02 atg... SEQ03 atc...
If there are enough sequences that the length of the prefix plus the length of the digit portion exceeds the length given to --anonymize, a warning will be given: aln-manipulations.pl -a 4 --prefix=SEQ # output SEQ1 atg... ... SEQ10 atc...
<code> # more output
WARNING: Anonymized ID length exceeded requested length: try a different length or prefix.</code>
- --composition, -w
-
Base or AA composition.
<code> Usage: bioseq -w input_file</code>
- --split, -S 'split_at'
-
Split the input sequence file into several smaller files with 'split_at' sequences per file. For instance, to split a file into several smaller files with 100000 sequences each, you would run:
<code> bioseq -S 100000 seq.fasta</code>
The output files will be named with the label "split_N" according to the input file (or with the STDIN prefix if the file is read via standard in), where N denotes the "part" or "split" number.
- --retrieveseq, -z 'sequence retriever using GenBank accession'
-
<code> Usage: bioseq -z [Accession]
Retrieves the sequence from GenBank using the provided GenBank accession. Prints out text in a fasta file.
EXAMPLE:
bioseq -z X83553
OUTPUT:
>X83553 B.garinii (PHei strain) opsC gene.
ATGAAAAAGAATACATTAAGTGCGATATTAATGACTTTATTTTTATTTATATCTTGTAAT
AATTCAGGTGGGGATACTGCATCTACTAATCCTGATGAGTCTGCGAAAGGACCTAATCTT
ATAGAAATAAGCAAAAAAATTACAGATTCTAATGCATTTGTACTGGCTGTGAAAGAAGTT
GAGGCTTTGATCTCATCTATAGATGAACTTGCTAATAAAGCTATTGGTAAAAAAATAAAT
CAAAATGGTTTAGATGCTGATGCTAATCACAACGGATCATTGTTAGCAGGAGCCCATGCA
ATATCAACTCTAATAAAACAAAAAACAGATGGATTGAAAGATCTAGAAGGGTTAAGTAAA
GAAATTGCAAAGGTGAAGGAATGTTCCGATAAATTTACTAAAAAGCTAACAGATAGTCAT
GCACAGCTTGGAGCAGTTGGTGGTGCTATTAATGATGATCGTGCAAAAGAAGCTATTTTA
AAAACACATGGGACTAACGATAAGGGTGCTAAAGAACTTAAAGAGTTATCTGAATCAGTA
GAAAGCTTGGCAAAAGCAGCTCAAGCAGCATTAGCTAATTCAGTTAAAGAGCTTACAAGT
CCTGTTGTGGCAGAAAGTCCAAAAAAACCTTAA</code>
- --dotplot, -D 'draw_dotplot'
-
Extract two sequences from input file and generate a dotplot.
<code> Usage: bioseq -D 'id1,id2,window_size,slider' fasta_file
</code>
Id1 and Id2 are extracted with their corresponding sequences. Be sure to use the entire sequence identifer, as this is a whole string match. Window_size corresponds to the number of character you would like to compare (Default window is 10). Slider is the number of windows to compare (Default slider is 10). The sequence corresponding to ID1 will appear on the X axis (row) and ID2 on the Y axis (column). This method will work on both DNA and Amino Acids.
<code> Example:
Sample Input:
>id1
ATACGA
>id2
ATACGA
Command: bioseq -D 'id1,id2,3'
Output:
A T A C G A
A *
T *
A *
C
G
A
A
C
A
A
T
G</code>
==item --rename, -R 'rename_id'
<code> Usage: bioseq -R [file_with_new_names] file_to_be_changed.fasta
Ex: bioseq -D list.txt test-bioseq.nuc
Input:
list.txt:
VS116:7:310:IGS:11 VS116
B31:1:100:IGS:11 B31
*Left column is the pattern to be replaced by the right column
file_to_be_changed.fasta:
>VS116:7:310:IGS:11
AATTTCAAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTGAAATTTTTCTAT
TGGATAAATTCTATACAAGAAGGTAAATA
>B31:1:100:IGS:11
AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA
TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA
Output:
>VS116
AATTTCAAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTGAAATTTTTCTAT
TGGATAAATTCTATACAAGAAGGTAAATA
>B31
AATTTTTAAAATATAATATAAAAACAGCTAATCCAATAGAAAAATTTTAAAACTTTTCTA
TTGGATAGATTTTATACAAAGAAGGTAATA</code>
Section under construction...