Southwest-University
Professor, Department of Biological Sciences, City University of New York, Hunter College & Graduate Center
Adjunct Faculty, Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Institute for Computational Biomedicine, Weil Cornell Medical College
Associate Professor, School of Life Science, South West University

Course Overview
Welcome to BioMedical Genomics, a computer workshop for advanced undergraduates and graduate students. A genome is the total genetic content of an organism. Driven by breakthroughs such as the decoding of the first human genome and next-generation DNA -sequencing technologies, biomedical sciences are undergoing a rapid and irreversible transformation into a highly data-intensive field.
Genome information is revolutionizing virtually all aspects of life sciences including basic research, medicine, and agriculture. Meanwhile, use of genomic data requires life scientists to be familiar with concepts and skills in biology, computer science, as well as data analysis.
This workshop is designed to introduce computational analysis of genomic data through hands-on computational exercises, using published studies.
The pre-requisites of the course are college-level courses in molecular biology, cell biology, and genetics. Introductory courses in computer programming and statistics are preferred but not strictly required.
Learning goals
By the end of this course successful students will be able to:
- Describe next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies & contrast it with traditional Sanger sequencing
- Explain applications of NGS technology including pathogen genomics, cancer genomics, human genomic variation, transcriptomics, meta-genomics, epi-genomics, and microbiome.
- Visualize and explore genomics data using RStudio
- Replicate key results using a raw data set produced by a primary research paper
Web Links
- Install R base: https://cloud.r-project.org
- Install R Studio (Desktop version): http://www.rstudio.com/download
- Download: R datasets
- A reference book: R for Data Science (Wickharm & Grolemund)
Quizzes and Exams
Student performance will be evaluated by attendance, three (4) quizzes and a final report:
- Attendance: 50 pts
- Assignments: 5 x 10 = 50 pts
- Quizzes: 2 x 25 pts = 50 pts
- Mid-term: 50 pts
- Final presentation: 50 pts
Total: 250 pts
Course Schedule
| Date & Hour | Tutorials | Assignment | Quiz & Exam | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 8 (Mon), 8:40-12:10 | Introduction; R Tutorial I;
File:R-part-1-small.pdf Lecture slides |
Assignment #1 (create a WORD document including scripts & graphs (i.e., compile your work into a lab report, due tomorrow)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| July 9 (Tu), 8:40-12:10 | R Tutorials II && III,
File:R-part-2.pdf Lecture slides |
Assignment #2
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| July 10 (Wed), 8:40-12:10 | R Tutorial IV
File:R-part-3.pdf Lecture slides |
Assignment #3
|
Quiz I | ||||||||||||||||||||
| July 11 (Thur), 8:40-12:10 | Intro to NGS; R Tutorial V |
Assignment #4
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| July 12 - 15 (Fri, Sat, Sun, Mon) | (Weekend Break) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| July 16 (Tu), 8:00-12:10 | Case Study 1. Fish microbiome | Quiz II | |||||||||||||||||||||
| July 17 (Wed), 8:00-12:10 | Case Study 2. Transcriptome | Assignment #5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
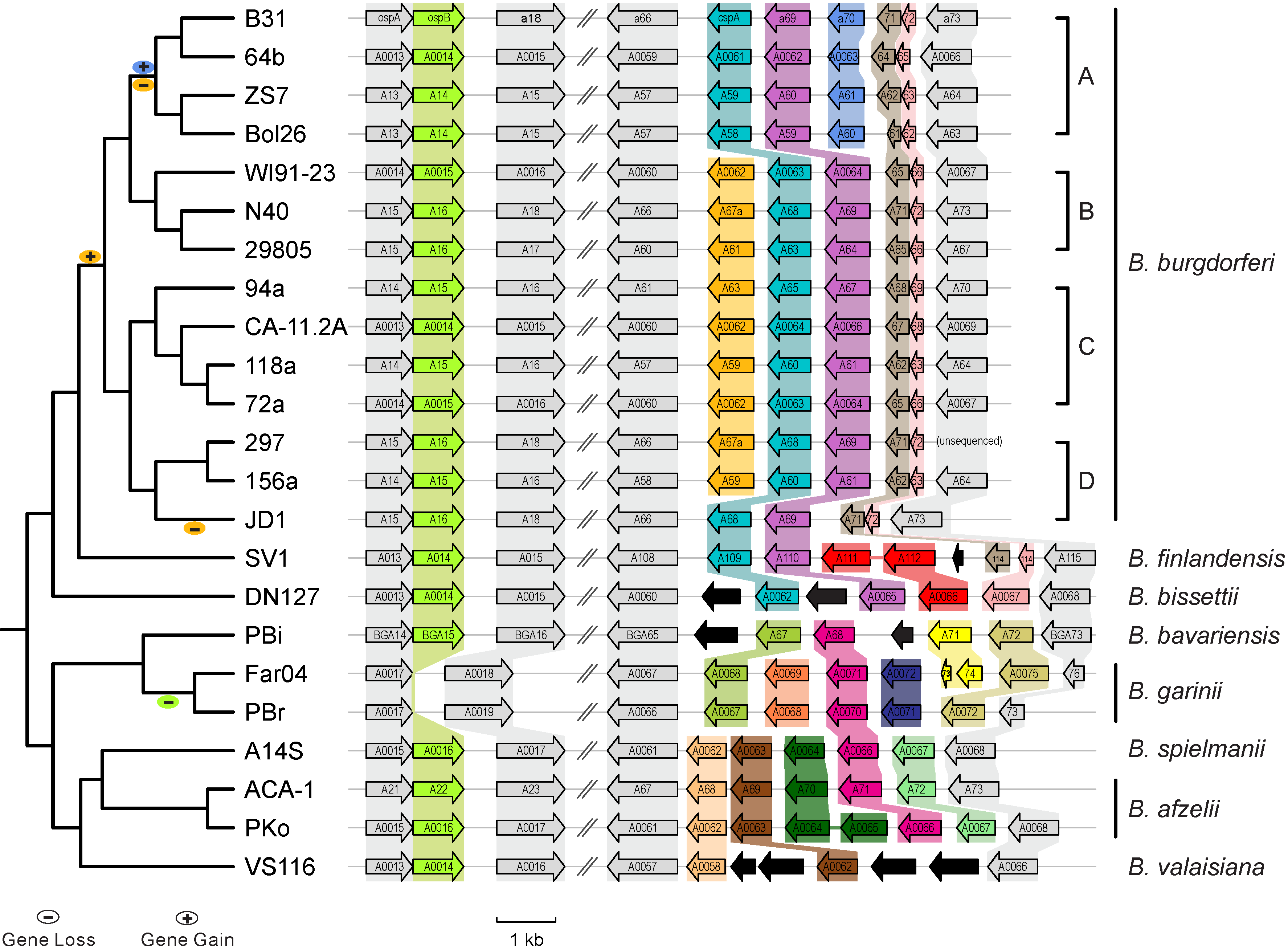
| July 18 (Thur), 8:00-12:10 | Case Study 3. Lyme Disease | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| July 19 (Fri), 8:00-12:10 | Presentations |
Papers & Datasets
| Omics Application | Paper link | Data set | NGS Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microbiome | Rimoldi_etal_2018_PlosOne | S1 Dataset | 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing |
| Transcriptome | Wang_etal_2015_Science | Tables S2 & S4 | RNA-Seq |
| Transcriptome & Regulome | Nava_etal_2019_BMCGenomics | Tables S2 & S3 | RNA-Seq & CHIP-Seq |
| Proteome | Qiu_etal_2017_NPJ | (to be posted) | SILAC |
| Population genomics (Lyme) | Di_etal_2018_JCM | Data & R codes | Amplicon sequencing (antigen locus) |
| Population genomics/GWAS (Human) | Simonti_etal_2016_Science | Table S2 | whole-genome sequencing (WGS); 1000 Genome Project (IGSR) |
| TB surveillance | Brow_etal_2015 | Sequence Archives | Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) |
| Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example | Example |