QuBi/modules/biol302: Difference between revisions
imported>Weigang mNo edit summary |
imported>Weigang |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Key Concepts2|Key Concepts]]=== | ===[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Key Concepts2|Key Concepts]]=== | ||
*Homology searching using BLAST | *Homology searching using BLAST ('''not Google''') | ||
*Mammalian gene | *Mammalian gene regulation | ||
So far, you have excised this XbaI fragment: | So far, you have excised this XbaI fragment: | ||
<div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:550px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:0px;"> | <div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:550px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:0px;"> | ||
CTAGATGCATTTACGAAGGAGACAGAAAACGTCTTTCGGCAATAGCTCTCAAATGCAAAACGACGTCGG | |||
CGAGCTGTCCCTTACCTGGAGGCCCGCAGGAGAAGCGCGGTGATCCGAGAGGGTCCCCCAGGGGTGTCCG | CGAGCTGTCCCTTACCTGGAGGCCCGCAGGAGAAGCGCGGTGATCCGAGAGGGTCCCCCAGGGGTGTCCG | ||
GTCGGTCTCCCGCTCGCCCAGCAGACGGCTGCGGAAACGGGGCAGCGTTTAAATAACCCCAGCTGGAGAC | GTCGGTCTCCCGCTCGCCCAGCAGACGGCTGCGGAAACGGGGCAGCGTTTAAATAACCCCAGCTGGAGAC | ||
ATGTCAGGACTTAGCTCCTCCGACAGCCGACGCCGGACGTGTCCCAACTTGACCAGCCCCACAGGAAGAG | ATGTCAGGACTTAGCTCCTCCGACAGCCGACGCCGGACGTGTCCCAACTTGACCAGCCCCACAGGAAGAG | ||
CTGAGTCAACTCGGCCCAGCCCAGTCCCACCCGTCCCGGAAGCCGCATCCCGGCGAGTCCGGGACCAGGC | CTGAGTCAACTCGGCCCAGCCCAGTCCCACCCGTCCCGGAAGCCGCATCCCGGCGAGTCCGGGACCAGGC | ||
ACCTGTCACCTCCTGGACCCCAGCAACGAGCCCAGCGCGACCCCGGAGCGGGCCCGAATTCT | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
=== | ---- | ||
===Gene identification using genome BLAST=== | |||
# Go to the NCBI-BLAST website at [http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastHome NCBI/BLAST Home Page] | # Go to the NCBI-BLAST website at [http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastHome NCBI/BLAST Home Page] | ||
# What is BLAST? Find the expanded answer by clicking on "more" | # What is BLAST? Find the expanded answer by clicking on "more" | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
# Copy and paste the above sequence into the "Enter Query Sequence" box | # Copy and paste the above sequence into the "Enter Query Sequence" box | ||
# Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click "BLAST" | # Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click "BLAST" | ||
# Wait for 10-30 seconds for the results to return ('''Be Patient'''). Once the result page is loaded, locate and copy the following information: | # Wait for 10-30 seconds for the results to return ('''Be Patient'''). Once the result page is loaded, locate and copy/write down the following information: | ||
## Species and strain | ## Species and strain | ||
## Chromosome | ## Chromosome | ||
## Length of your query sequence | ## Length of your query sequence | ||
## Sequence identity, number of matched bases, and number of gaps between the matched sequences | ## Sequence identity, number of matched bases, and number of gaps between the matched sequences | ||
# Click the link for "5' side" (next to '''Features''') will bring you a standard GenBank file of this gene. Locate and copy the following structural information about this gene: | |||
# Click the link for "5' side" | |||
## Gene accession (ID number) | ## Gene accession (ID number) | ||
## Total length of the gene | ## Total length of the gene | ||
## Number of introns | ## Number of introns | ||
## Which is the | ## Which is the non-template (mRNA analog) strand: the above sequence itself or its reverse complement? [Hint: note the word '''complement''' in mRNA and cDNA lines) | ||
---- | ---- | ||
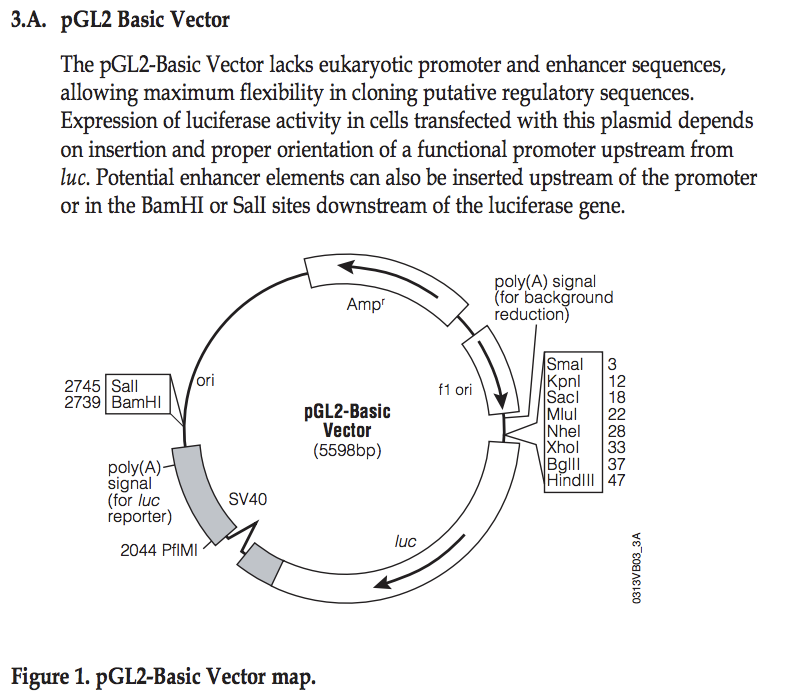
===Explore pGL2 vector=== | |||
This sequence has been cloned into the NheI site in the pGL2basic vector | This sequence has been cloned into the NheI site in the pGL2basic vector: | ||
<div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:400px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:10px;"> | <div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:400px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:10px;"> | ||
[[File: | [[File:PGL2vector-map.png|400px]] | ||
''[http://www.promega.com/ | ''[http://www.promega.com/~/media/Files/Resources/Protocols/Technical%20Manuals/0/pGL2%20Luciferase%20Reporter%20Vectors%20Protocol.pdf Source: Promega]'' | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
# Identify the location | # Identify the location where you have cloned your fragment | ||
# What are the two possible directions (with respect to the luciferase gene) you may have cloned your fragment? | |||
# From the PDF file, find the location of the EcoRI site | # From the PDF file, find the location of the EcoRI site | ||
---- | ---- | ||
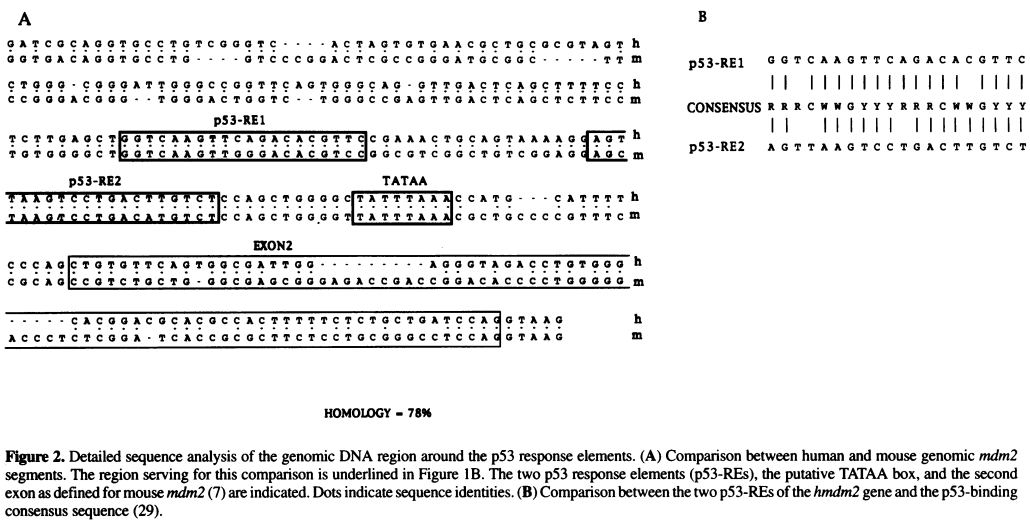
===Identify regulatory elements through literature search=== | |||
<div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:800px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:0px;"> | <div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:800px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:0px;"> | ||
[[File:Zauberman_fig2.png|800px]] | [[File:Zauberman_fig2.png|800px]] | ||
''Source:'' Zauberman et al. "A functional p53-responsive intronic promoter is contained within the human mdm2 gene". Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 July 25; 23(14): 2584–2592. ''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC307078/ Pubmed] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC307078/pdf/nar00014-0022.pdf PDF]'' | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
# Identify TATA box in the above sequence by looking for AT-rich regions | # Identify the TATA box in the above sequence by looking for AT-rich regions | ||
# Once the TATA box is located, use this sequence as the anchor point to locate other elements, including the | # Once the TATA box is located, use this sequence as the anchor point to locate other elements, including the two p53 Response Element (p53 RE) sites and the Exon 2 | ||
# Locate the EcoRI restriction site using the [http://tools.neb.com/NEBcutter2/ NEBcutter website] | # Locate the EcoRI restriction site using the [http://tools.neb.com/NEBcutter2/ NEBcutter website] | ||
# What are the expected | # What are the expected EcoRI fragment sizes for the two possible orientations of your cloned DNA? | ||
# | # Which orientation would you expect to give higher luciferase expression? | ||
---- | ---- | ||
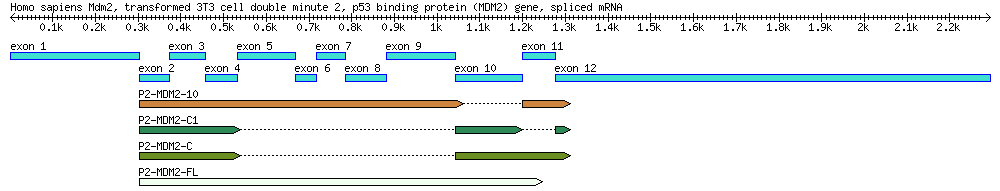
==[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Part 2: Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST|Part | ==[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Part 2: Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST|Part 2 (Extra Credit Assignment): Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST]]== | ||
<div | <div style="font-family:Monospace;line-height:1;width:800px;border-style:solid;border-width:1px;border-color:#AAAAFF;background-color:#EEEEFF;padding-left:5px;padding-right:5px;padding-top:0px;padding-bottom:0px;"> | ||
[[File:4seq.png|800px]] | [[File:4seq.png|800px]] | ||
A diagram of the MDM2 gene used in this exercise, along with its splice variants. By the end of this module you will create a similar diagram. ''Reference:'' Arva NC, Talbott KE, Okoro DR, Brekman A, Qiu WG, Bargonetti J. 2008. Disruption of the p53-Mdm2 complex by Nutlin-3 reveals different cancer cell phenotypes. Ethnicity and Disease. 18(S2):1-8. | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Objectives|Key Concepts]]=== | |||
* Use BLAST ('''not Google''') to find matches of DNA and protein sequences | |||
* Alternative splicing and isoforms of a single gene | |||
===[[QuBi/modules/biol302#Objectives| | You will use the following table for your exercise: | ||
* | |||
* | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! Genbank Accession # !! cDNA Clone !! Description !! Cell Line !! Length (bp) | ! Genbank Accession # !! cDNA Clone !! Description !! Cell Line !! Length (bp) | ||
| Line 92: | Line 83: | ||
| AF527840 || || Genomic DNA || || 34,088 | | AF527840 || || Genomic DNA || || 34,088 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| EU076746 || P2-MDM2-C1 || cDNA | | EU076746 || P2-MDM2-C1 || cDNA || MANCA || 427 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| EU076747 || P2-MDM2-10 || cDNA | | EU076747 || P2-MDM2-10 || cDNA || ML-1 || 842 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| EU076748 || P2-MDM2-C || cDNA | | EU076748 || P2-MDM2-C || cDNA || A876 || 505 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| EU076749 || P2-MDM2-FL || | | EU076749 || P2-MDM2-FL || cDNA || SJSA-1 || 845 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===Explore the GenBank file=== | |||
#Search [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Nucleotide GenBank] using the accession AF527840. Read the GenBank file and find out from the feature table how many introns and exons this sequence has according to the "mRNA" and "CDS" features. | |||
# DRAW a diagram of this gene using the information and coordinates listed in the annotation. | |||
# DRAW a diagram of this gene using the information and coordinates listed in the annotation. | ##Label the top of the diagram with basic information, such as the gene's name and species information. | ||
##Label the top of the diagram with basic information, such as the gene's name | ##Label coordinates for introns, exons, 3'/5' UTRs,start-codon, and stop-codon coordinates. | ||
## | |||
##Draw the diagram mostly to scale. It does NOT have to be perfect, but make a reasonable effort. Put a scale bar and length markers on your drawing. | ##Draw the diagram mostly to scale. It does NOT have to be perfect, but make a reasonable effort. Put a scale bar and length markers on your drawing. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===Explore the graphical presentation of the gene=== | |||
Genbank provides graphical representations of the sequences on its database: click the "Graphics" link below the sequence title, OR click "Display Settings" above the title, and choose "Graphics". Take a few minutes to explore this graphical | Genbank provides graphical representations of the sequences on its database: click the "Graphics" link below the sequence title, OR click "Display Settings" above the title, and choose "Graphics". Take a few minutes to explore this graphical and compare it with your diagram. | ||
---- | |||
# | ===Use BLAST to determine which exons are used in the mRNA transcript=== | ||
# | This is the most "bioinformatic" part of the assignment. Blast one of the mRNA sequences (EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749) against the main sequence (AF527840) and use the results to answer the following questions. Suggested procedures: | ||
# Go to the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ NCBI BLAST] website | |||
# Click the link “Align two (or more) sequences using BLAST (bl2seq)” under “Specialized BLAST” (near the page bottom) | |||
# In the “Sequence 1” text box, type “AF527840” (the accession for the genomics). Fill in “from 1” and “to 34088”. In the “Sequence 2” text box, type in "EU076748" (or other cDNA accession in the table). Fill in the “from” box with 1 and the “to” box with 505. | |||
# Click “Align”. You should get a “Blast Result” output page. | |||
# Interpret your results: | |||
## Which exons are present and which ones are absent in EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749? (Hint: Refer to the mRNA join statement). | |||
## Explain the following BLAST terms: “Expect” (e-value), “Identities”, “Gap”, “Strand” | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 14:50, 23 March 2013
- BIOL 302 Lab (Bioinformatics Exercises)
Research in molecular genetics requires effective use of bioinformatic tools to analyze and understand the genetic materials being worked with. The following exercises will expose you to real-world scenarios and introduce you to the methods and tools you can use to solve these problems.
Part 1: Cloning of murine mdm2 gene sequence to study cis acting DNA elements
Key Concepts
- Homology searching using BLAST (not Google)
- Mammalian gene regulation
So far, you have excised this XbaI fragment:
CTAGATGCATTTACGAAGGAGACAGAAAACGTCTTTCGGCAATAGCTCTCAAATGCAAAACGACGTCGG CGAGCTGTCCCTTACCTGGAGGCCCGCAGGAGAAGCGCGGTGATCCGAGAGGGTCCCCCAGGGGTGTCCG GTCGGTCTCCCGCTCGCCCAGCAGACGGCTGCGGAAACGGGGCAGCGTTTAAATAACCCCAGCTGGAGAC ATGTCAGGACTTAGCTCCTCCGACAGCCGACGCCGGACGTGTCCCAACTTGACCAGCCCCACAGGAAGAG CTGAGTCAACTCGGCCCAGCCCAGTCCCACCCGTCCCGGAAGCCGCATCCCGGCGAGTCCGGGACCAGGC ACCTGTCACCTCCTGGACCCCAGCAACGAGCCCAGCGCGACCCCGGAGCGGGCCCGAATTCT
Gene identification using genome BLAST
- Go to the NCBI-BLAST website at NCBI/BLAST Home Page
- What is BLAST? Find the expanded answer by clicking on "more"
- Since BLAST finds matches (homologous sequences) between biological sciences, it needs a "query" sequence as input as well as a "database" to search against. To find the matches to the above sequence, what would be your "query" sequence and what would be your "database"?
- Start BLASTing against the mouse genome by clicking "Mouse" under "BLAST Assembled RefSeq Genomes"
- Copy and paste the above sequence into the "Enter Query Sequence" box
- Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click "BLAST"
- Wait for 10-30 seconds for the results to return (Be Patient). Once the result page is loaded, locate and copy/write down the following information:
- Species and strain
- Chromosome
- Length of your query sequence
- Sequence identity, number of matched bases, and number of gaps between the matched sequences
- Click the link for "5' side" (next to Features) will bring you a standard GenBank file of this gene. Locate and copy the following structural information about this gene:
- Gene accession (ID number)
- Total length of the gene
- Number of introns
- Which is the non-template (mRNA analog) strand: the above sequence itself or its reverse complement? [Hint: note the word complement in mRNA and cDNA lines)
Explore pGL2 vector
This sequence has been cloned into the NheI site in the pGL2basic vector:
- Identify the location where you have cloned your fragment
- What are the two possible directions (with respect to the luciferase gene) you may have cloned your fragment?
- From the PDF file, find the location of the EcoRI site
Identify regulatory elements through literature search
Source: Zauberman et al. "A functional p53-responsive intronic promoter is contained within the human mdm2 gene". Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 July 25; 23(14): 2584–2592. Pubmed PDF
- Identify the TATA box in the above sequence by looking for AT-rich regions
- Once the TATA box is located, use this sequence as the anchor point to locate other elements, including the two p53 Response Element (p53 RE) sites and the Exon 2
- Locate the EcoRI restriction site using the NEBcutter website
- What are the expected EcoRI fragment sizes for the two possible orientations of your cloned DNA?
- Which orientation would you expect to give higher luciferase expression?
Part 2 (Extra Credit Assignment): Identification of mdm2 Splice Variants Using BLAST
A diagram of the MDM2 gene used in this exercise, along with its splice variants. By the end of this module you will create a similar diagram. Reference: Arva NC, Talbott KE, Okoro DR, Brekman A, Qiu WG, Bargonetti J. 2008. Disruption of the p53-Mdm2 complex by Nutlin-3 reveals different cancer cell phenotypes. Ethnicity and Disease. 18(S2):1-8.
Key Concepts
- Use BLAST (not Google) to find matches of DNA and protein sequences
- Alternative splicing and isoforms of a single gene
You will use the following table for your exercise:
| Genbank Accession # | cDNA Clone | Description | Cell Line | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF527840 | Genomic DNA | 34,088 | ||
| EU076746 | P2-MDM2-C1 | cDNA | MANCA | 427 |
| EU076747 | P2-MDM2-10 | cDNA | ML-1 | 842 |
| EU076748 | P2-MDM2-C | cDNA | A876 | 505 |
| EU076749 | P2-MDM2-FL | cDNA | SJSA-1 | 845 |
Explore the GenBank file
- Search GenBank using the accession AF527840. Read the GenBank file and find out from the feature table how many introns and exons this sequence has according to the "mRNA" and "CDS" features.
- DRAW a diagram of this gene using the information and coordinates listed in the annotation.
- Label the top of the diagram with basic information, such as the gene's name and species information.
- Label coordinates for introns, exons, 3'/5' UTRs,start-codon, and stop-codon coordinates.
- Draw the diagram mostly to scale. It does NOT have to be perfect, but make a reasonable effort. Put a scale bar and length markers on your drawing.
Explore the graphical presentation of the gene
Genbank provides graphical representations of the sequences on its database: click the "Graphics" link below the sequence title, OR click "Display Settings" above the title, and choose "Graphics". Take a few minutes to explore this graphical and compare it with your diagram.
Use BLAST to determine which exons are used in the mRNA transcript
This is the most "bioinformatic" part of the assignment. Blast one of the mRNA sequences (EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749) against the main sequence (AF527840) and use the results to answer the following questions. Suggested procedures:
- Go to the NCBI BLAST website
- Click the link “Align two (or more) sequences using BLAST (bl2seq)” under “Specialized BLAST” (near the page bottom)
- In the “Sequence 1” text box, type “AF527840” (the accession for the genomics). Fill in “from 1” and “to 34088”. In the “Sequence 2” text box, type in "EU076748" (or other cDNA accession in the table). Fill in the “from” box with 1 and the “to” box with 505.
- Click “Align”. You should get a “Blast Result” output page.
- Interpret your results:
- Which exons are present and which ones are absent in EU076746, EU076747, EU076748, EU076749? (Hint: Refer to the mRNA join statement).
- Explain the following BLAST terms: “Expect” (e-value), “Identities”, “Gap”, “Strand”